Yarkovsky effect
Yarkovsky effect
This is important because it's something that can change the course of an asteroid. NASA takes this into consideration in trying to determine the chances of a rogue asteroid colliding with the Earth.
A Russian civil engineer, Ivan Osipovich Yarkovsky, discovered this phenomenon in 1900. It has to do with the diurnal heating of a rotating object in space. Basically, it's how sunlight affects the course of an asteroid by heating one side of an asteroid and causing this to act as pushing effect.
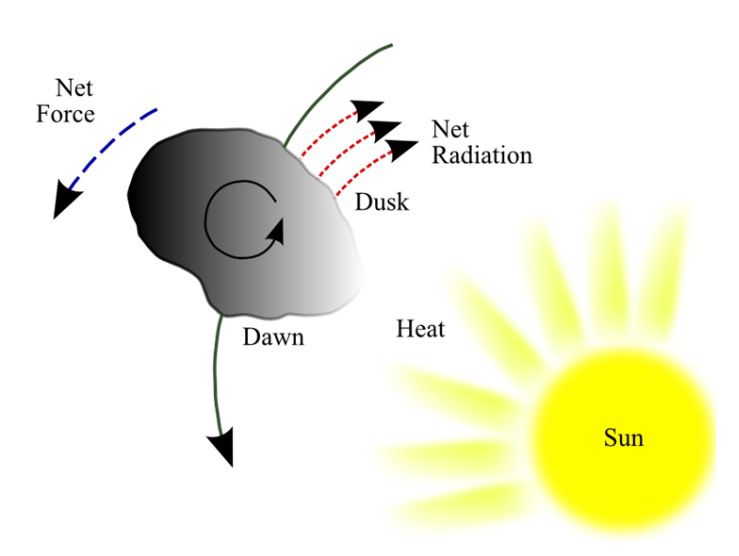
Diurnal effect is where the sun warms a rotating body by solar radiation during the day, and it cools at night. There is a lag in the emission of this radiation at night versus how quickly it heats up during the day. This effect applies to both the Earth and an asteroid. The side that cools emits thermal photons (infrared) that are not as effective in pushing like the sun's thermal photons are. The overall effect is to cause the asteroid to spiral away from the sun. This applies to prograde rotators, asteroids that rotate in the same direction they are orbiting. Retrograde rotating asteroids suffer the opposite effect and fall towards the sun.
The Earth is way too big for this to be a problem.
Basically, you could think of this as the sun pushing the asteroid around by the effect of anisotropic (directional) emission of thermal photons, which carry momentum.
Where this becomes a problem is if this effect is causing an asteroid to change its orbit so that it collides with Earth. One such asteroid is 1999 RQ36, which is one-third of a mile in diameter. The sun has altered this asteroid's course over 12 years by the Yarkovsky effect. Its orbit has been changed by 100 miles over this time period, and since this asteroid crosses Earth's orbit, it could present a possible threat.
Now, even when this asteroid is nearest to the sun, the Yarkovsky effect is only equivalent to a half-ounce. This doesn't sound like much but over a long period of time it adds up, and since this asteroid crossed near Earth 11 times from 1654 to 2135, its massive size (68 tons) could be a problem in 2135 when it will be within 220,000 miles of Earth, which is closer than the moon.
Thanks for reading.
Bạn đang đọc truyện trên: AzTruyen.Top