Lagrangian Point
Lagrangian Point
What the heck is the Lagrangian point?
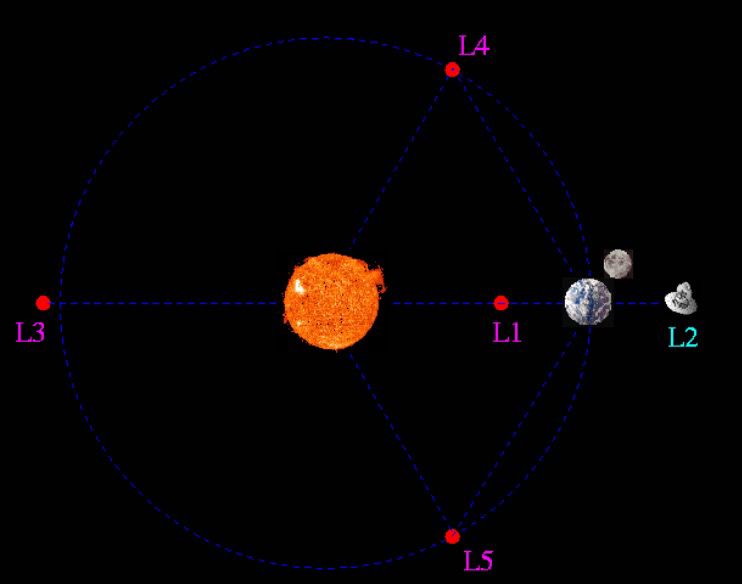
Actually, there is more than one Lagrange point. There are five. A Lagrangian point is a location between two large orbiting objects where the gravity force between both of them creates a stable position. In other words an object that is caught in one of these Lagrange points is provided the exact amount of centripetal force to orbit both of the larger objects.
The L4 and L5 Lagrange points seem to be important. Some planets have minor bodies near these points. The L4 and L5 points create an equilateral triangle with the major body. In the case of the Sun-Earth system, the L4 and L5 points lie at opposite sides of two equilateral triangles. Satellites in these positions are in stable orbits.

On the other hand the L1, L2 and L3 are Lagrange points that are unstable. Satellites or spacecraft in these locations will fall out of orbit unless correctional burns are done to prevent it. These positions are however interesting places. In the case of the Sun-Earth system, L1 is a position that is never shadowed by either the Earth or the moon. The L2 position is great because it maintains the same position relative to both the Sun and Earth. A satellite in the L3 position is unstable but it's a good place to observe the Sun because it can spot solar flares on the Sun before they rotate into a location that could threaten Earth.
There is a known asteroid in the Sun-Earth L4 and L5 Lagrange points as well as interplanetary dust. As it turns out this is true for many systems, such as the Saturn moon, Tethys, which has two smaller moons (Telesto and Calypso) in its L4 - L5 locations.
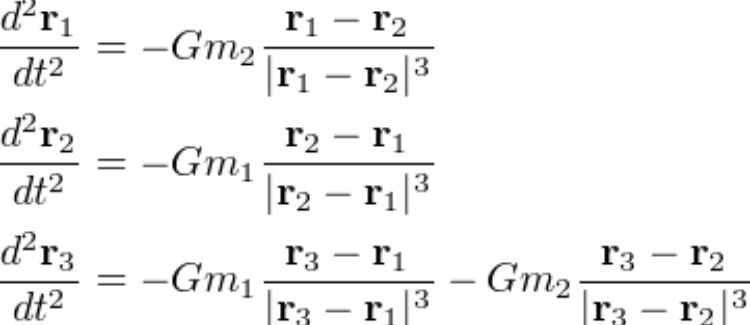
Calculating where these locations is complicated, but equations have been worked out and involve the masses of the two major orbiting objects and the distance between them. Some of the equations reduce the three-body system to points on a sphere.
The reason that this is important is because several important spacecraft have been sent to these locations in the Sun-Earth system to observe the Sun and Earth from stable orbits, making obtaining good high resolution images easier. The L2 Sun-Earth location is also a great place to park a space observatory, and in fact there are several there already and the James Webb Space Telescope is slated be sent there.
So, the reason that Lagrange points are important is that they provide stable orbits.
Thanks for reading.
Bạn đang đọc truyện trên: AzTruyen.Top